In today’s digital world, terms like UI and UX design are often used interchangeably, but they represent two distinct disciplines that are essential to creating a successful product. Whether you’re building a website, a mobile app, or any digital platform, understanding the difference between UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) design can profoundly impact the outcome.
What is UI Design?
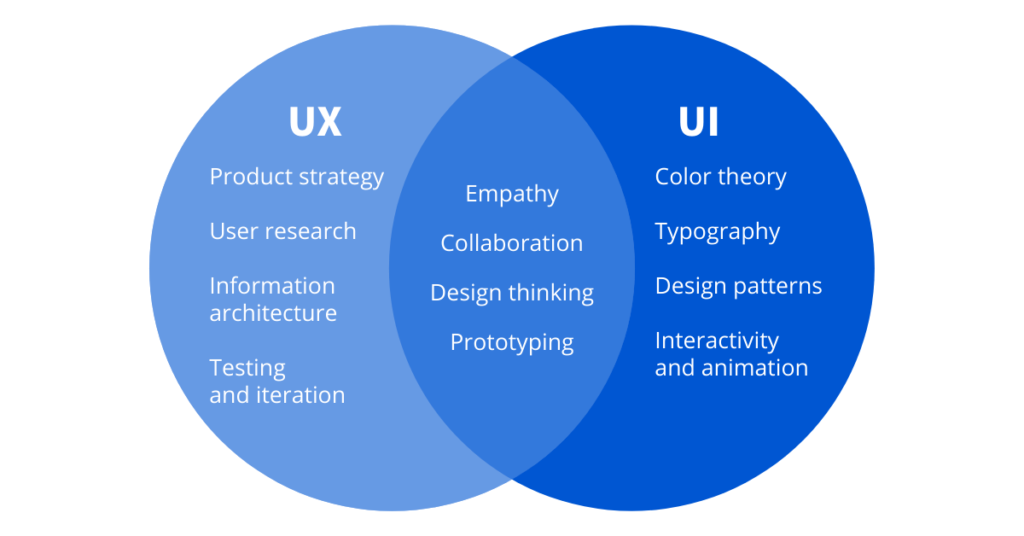
UI, or User Interface design, refers to the look and feel of a product’s interface. It involves the aesthetics of a digital product and how users interact with it visually. UI design focuses on designing each page or screen of an app or website, paying attention to the buttons, icons, typography, color schemes, and overall visual hierarchy.
In UI design, the goal is to make the interface not only beautiful but also functional and user-friendly. Every element must be visually appealing and aligned with the brand’s identity while serving a practical purpose. For example, a UI designer might choose a specific shade of blue because it conveys trust, or use a particular typeface to improve readability.
Main Components of UI Design
- Colors – Colors affect how users feel about the product and guide them to take specific actions.
- Typography – The style, size, and layout of fonts make text legible and aesthetically pleasing.
- Buttons and Icons – Buttons should be clear and functional, while icons offer visual cues to actions.
- Spacing and Layout – Proper spacing creates balance and ensures a smooth flow of information.
- Consistency – Consistency in design elements helps users understand the interface and reduces cognitive load.
Example of UI in Action
Consider a banking app. The UI designer is responsible for the overall appearance: the color scheme that aligns with the brand, the size and style of the buttons to make them easy to press, and the spacing of elements to ensure users don’t feel overwhelmed. Essentially, UI design is about how the product looks and works visually.
What is UX Design?
While UI design focuses on how things look, UX design is about how things work and feel. UX stands for User Experience and refers to the overall interaction a user has with a product or service. UX design focuses on understanding the needs of the user and creating a seamless, intuitive experience that meets those needs efficiently.
A UX designer’s job begins with user research—understanding the target audience, their problems, and how the product can solve them. They focus on functionality, ease of navigation, user flows, and removing obstacles that might prevent users from achieving their goals.
Main Components of UX Design
- User Research – Identifying user needs, behaviors, and pain points through surveys, interviews, and analytics.
- Wireframing and Prototyping – Creating simple, low-fidelity mockups of the product to test its structure and flow.
- Usability Testing – Testing the product with real users to identify potential problems or areas for improvement.
- User Flows – Designing the paths users take to complete tasks, ensuring it’s as smooth and straightforward as possible.
- Feedback and Iteration – Continuously refining the product based on user feedback to improve the overall experience.
Example of UX in Action
Let’s return to the banking app. The UX designer ensures that when a user wants to transfer money, they can easily find the transfer option, input the necessary information, and complete the process without frustration. If users struggle to find or use key features, it reflects a failure in UX, even if the UI design is visually perfect.
Key Differences Between UI and UX Design
Though UI and UX design are closely related and often work together, they are fundamentally different in their focus and goals. Here are the key differences:
- UI is Visual, UX is Functional: UI design is all about how things look, whereas UX design is about how things work.
- UI is Part of UX, But Not All of It: While the UI contributes to the overall user experience, it’s just one aspect. UX encompasses the entire journey of a user interacting with a product, from their first impression to the moment they achieve their goal.
- UI Focuses on Aesthetics, UX on Usability: A UI designer is concerned with colors, typography, and visual elements, while a UX designer focuses on user flows, functionality, and how intuitive the experience is.
How UI and UX Work Together
UI and UX design must work in harmony to create a successful product. A visually stunning interface (UI) is worthless if users struggle to navigate it (poor UX). Likewise, a highly functional product that solves user problems but looks outdated or cluttered may not attract users in the first place.
Think of a restaurant: UX design is like the service, ambiance, and menu that provide a pleasant dining experience. UI design, on the other hand, is the beautiful presentation of the dishes and decor of the restaurant. Both contribute to the overall dining experience.
A great UI can elevate the user’s impression of a product, while strong UX ensures that the product delivers on its promise.
Visual Example
Imagine using a photo editing app. The UI would include the buttons, sliders, and icons that allow users to adjust their photos. The UX ensures that these controls are intuitive, responsive, and easy to navigate, so users can quickly and efficiently edit their images.
Why the Difference Matters for Businesses
For businesses, understanding the distinction between UI and UX design is crucial. Investing in one without the other can lead to poor results. A product with a sleek design but poor usability will frustrate users and lead to high drop-off rates. Conversely, a highly functional product with an unattractive interface may not engage users or compete in a crowded market.
Business Benefits of UI/UX
- Improved User Satisfaction: When users enjoy both how a product looks and how it works, they are more likely to engage with it and return.
- Increased Conversion Rates: A smooth user experience with an attractive interface encourages users to complete desired actions, whether that’s making a purchase or signing up for a service.
- Customer Retention: An intuitive and pleasant design leads to happy customers who are more likely to remain loyal to your product or service.
- Competitive Edge: In a saturated market, businesses that pay attention to both UI and UX stand out from the competition.
Common Misconceptions About UI and UX
There are several myths and misconceptions about UI and UX design that need clarification:
- UI is just about making things look pretty: UI design involves much more than choosing colors and fonts; it’s about ensuring the product is intuitive and visually coherent.
- UX is only about usability testing: While testing is important, UX design encompasses everything from user research to prototyping and iteration.
- UX designers don’t need to care about visuals: While UX focuses on functionality, understanding basic visual design principles is crucial for ensuring smooth collaboration with UI designers.
The Importance of Hiring the Right Talent
It’s essential to hire the right people when building digital products. If your product needs to focus heavily on visuals, you may prioritize a UI designer, whereas complex user journeys and functionality require a skilled UX designer.
Many companies mistakenly believe that one person can handle both roles. While some designers have skills in both areas, it’s often beneficial to have dedicated experts to ensure that both UI and UX aspects are fully optimized.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between UI and UX design is essential for anyone involved in the creation of digital products. UI design focuses on the look and feel, while UX design is about the overall experience and functionality. Both are crucial to building products that not only attract users but also keep them engaged.
By investing in both UI and UX design, businesses can ensure they create products that are not only visually appealing but also easy to use, ultimately leading to higher user satisfaction and business success.